A growing concern about arsenic in rice highlights the need for vigilance in food safety, echoing broader themes of moderation and caution in knowledge application.
Quick Take
- Rising concern over arsenic levels in rice sparks consumer and scientific interest.
- Experts stress the importance of moderation and informed decision-making.
- Historical lessons on unchecked knowledge guide current food safety debates.
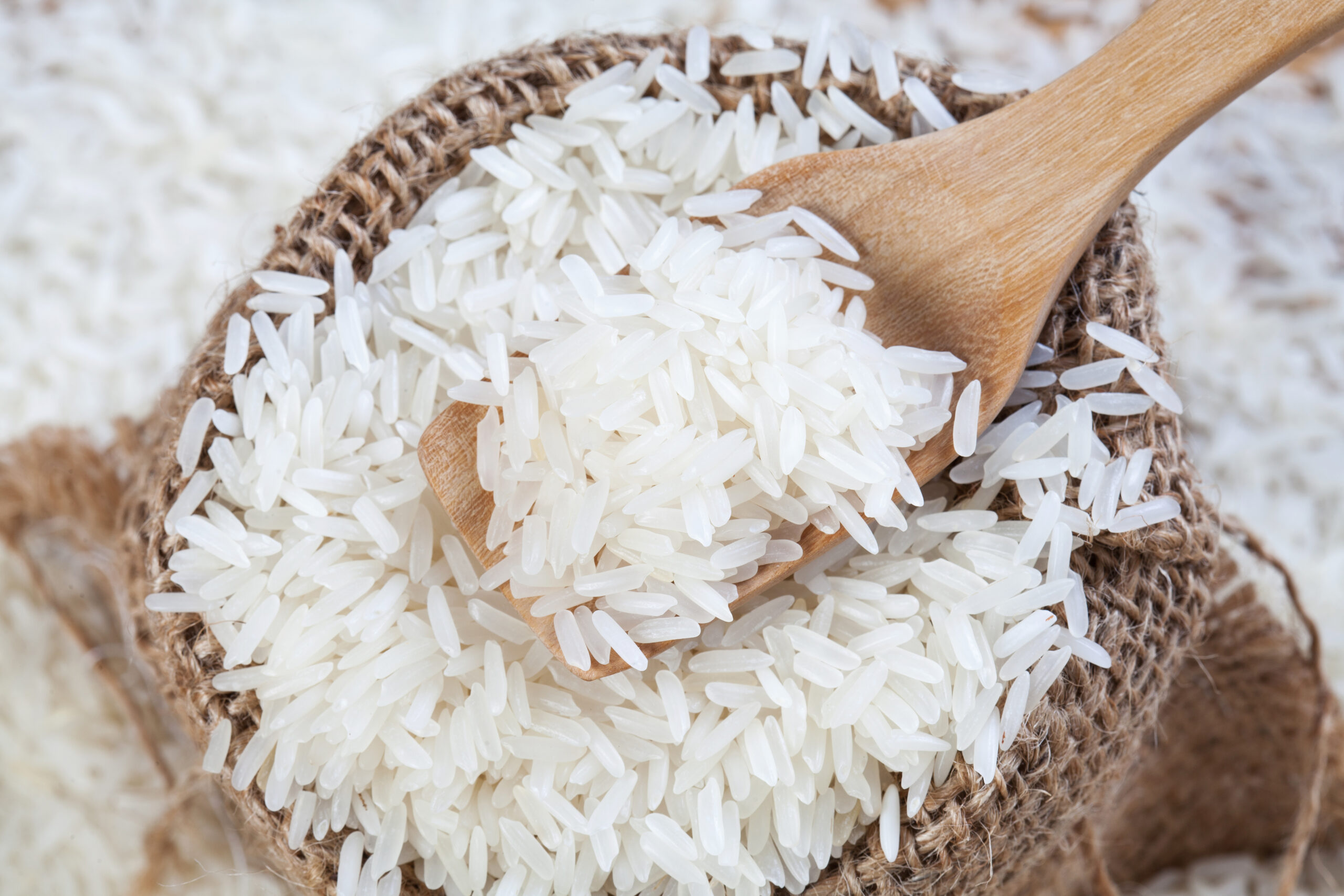
Understanding the Arsenic in Rice Issue
Concerns about arsenic in rice are amplifying, with consumers and experts alike delving into food safety implications. Rice, a staple for billions, naturally absorbs arsenic from the soil and water it grows in, which poses potential health risks. The issue underscores the necessity of moderation and informed caution, echoing the longstanding debate on balancing knowledge with responsibility. Moderation in consumption and processing methods can mitigate health risks, reflecting ancient wisdom on the prudent application of knowledge.
Historically, the unchecked application of knowledge has led to unintended harm, as seen in various technological advancements. The Enlightenment era, though celebrated for its embrace of reason, also initiated challenges that we continue to address today. In the context of rice consumption, this historical perspective emphasizes the importance of balancing scientific progress with ethical considerations, ensuring that food safety standards are both robust and adaptable.
Watch:
Current Developments in Food Safety
Recent developments in food safety regulations illustrate an ongoing commitment to address arsenic concerns. Governments and scientific bodies are actively refining guidelines to limit arsenic exposure, advocating for diverse diets and improved agricultural practices. Public awareness campaigns stress the need to wash and cook rice thoroughly, reducing arsenic levels significantly. These efforts align with broader regulatory trends seeking to balance innovation with public safety, a theme increasingly relevant in our rapidly advancing world.
As regulatory frameworks evolve, they often lag behind technological advancements, highlighting a critical gap in timely intervention. Ethical review boards and scientific advisory groups are becoming more prominent, tasked with ensuring that safety guidelines keep pace with new discoveries. This dynamic mirrors the broader dialogue on moderating knowledge application, as societies strive to harness the benefits of scientific progress while safeguarding public health.
Several major rivers flowing across the border from Myanmar to Thailand have been contaminated with dangerously high levels of arsenic, threatening to cause a public health crisis.
Read more: https://t.co/fQCdKx5s8C
— SBS News (@SBSNews) September 6, 2025
Expert Perspectives on Moderation
Experts in food science and policy advocate for moderation in both consumption patterns and regulatory approaches. They emphasize the critical role of informed decision-making, urging consumers to remain vigilant without succumbing to undue alarm. This balanced perspective is crucial in navigating the complexities of modern food systems, where scientific insights must be carefully integrated into everyday choices. By fostering greater public understanding, stakeholders aim to empower individuals and communities to make informed decisions about their diets, reflecting a broader commitment to responsible knowledge application.
In conclusion, the arsenic in rice debate serves as a microcosm of the broader challenges associated with knowledge application. It highlights the importance of moderation, not only in dietary habits but also in regulatory practices and scientific exploration. Through ongoing dialogue and cooperation among stakeholders, societies can navigate these challenges, ensuring that the pursuit of knowledge remains a force for good, rather than a source of unintended harm.
Sources:
Understanding Moderation in Research
Mediation and Moderation Analyses
Moderation Variables in Organizational Behavior
Educational Research on Moderation
Moderation Analysis with Hayes Process Macro