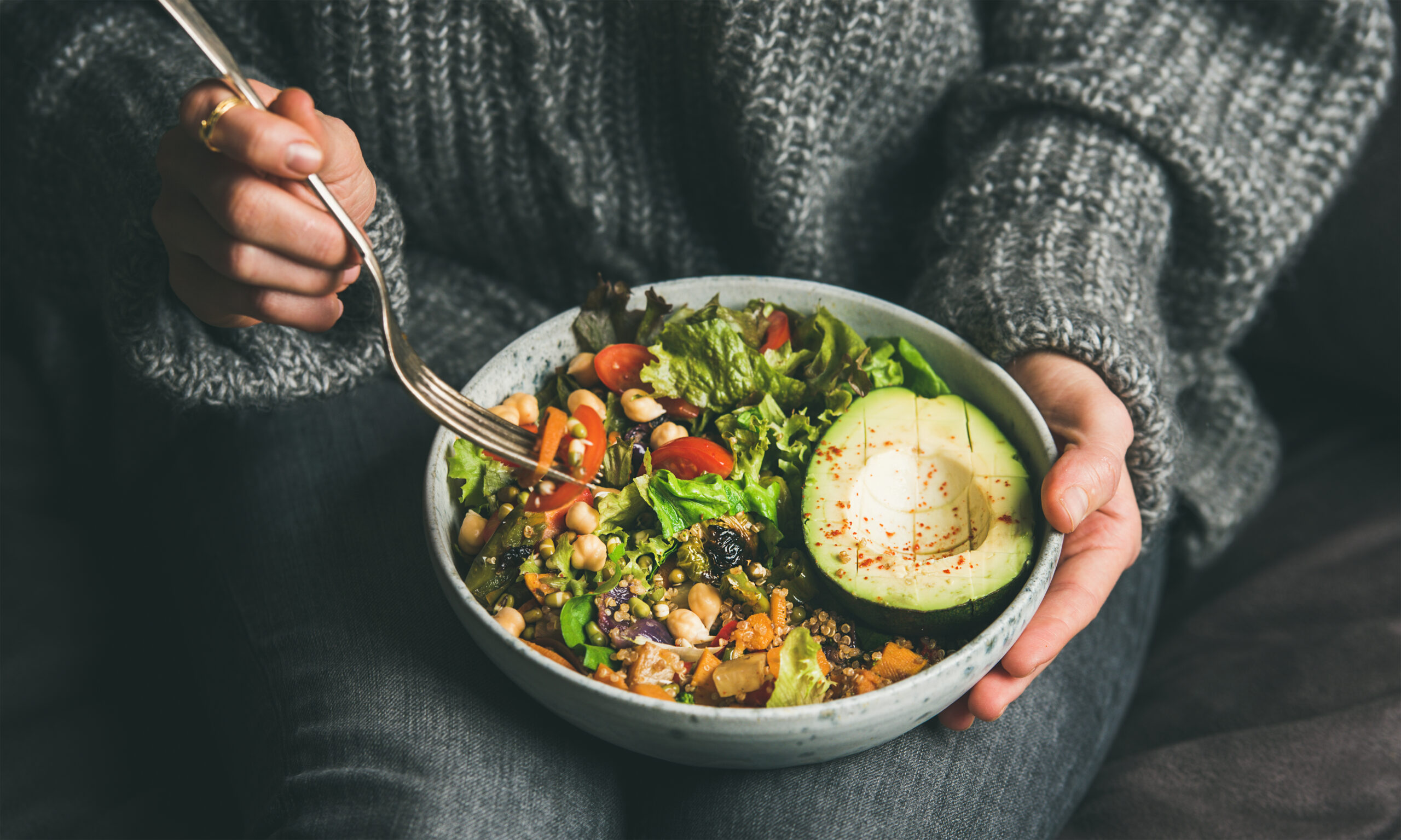
Your blood pressure doesn’t need pharmaceutical intervention when seven clinically proven natural strategies can reduce systolic readings by 5-10 points or more, rivaling the effectiveness of many medications.
Quick Take
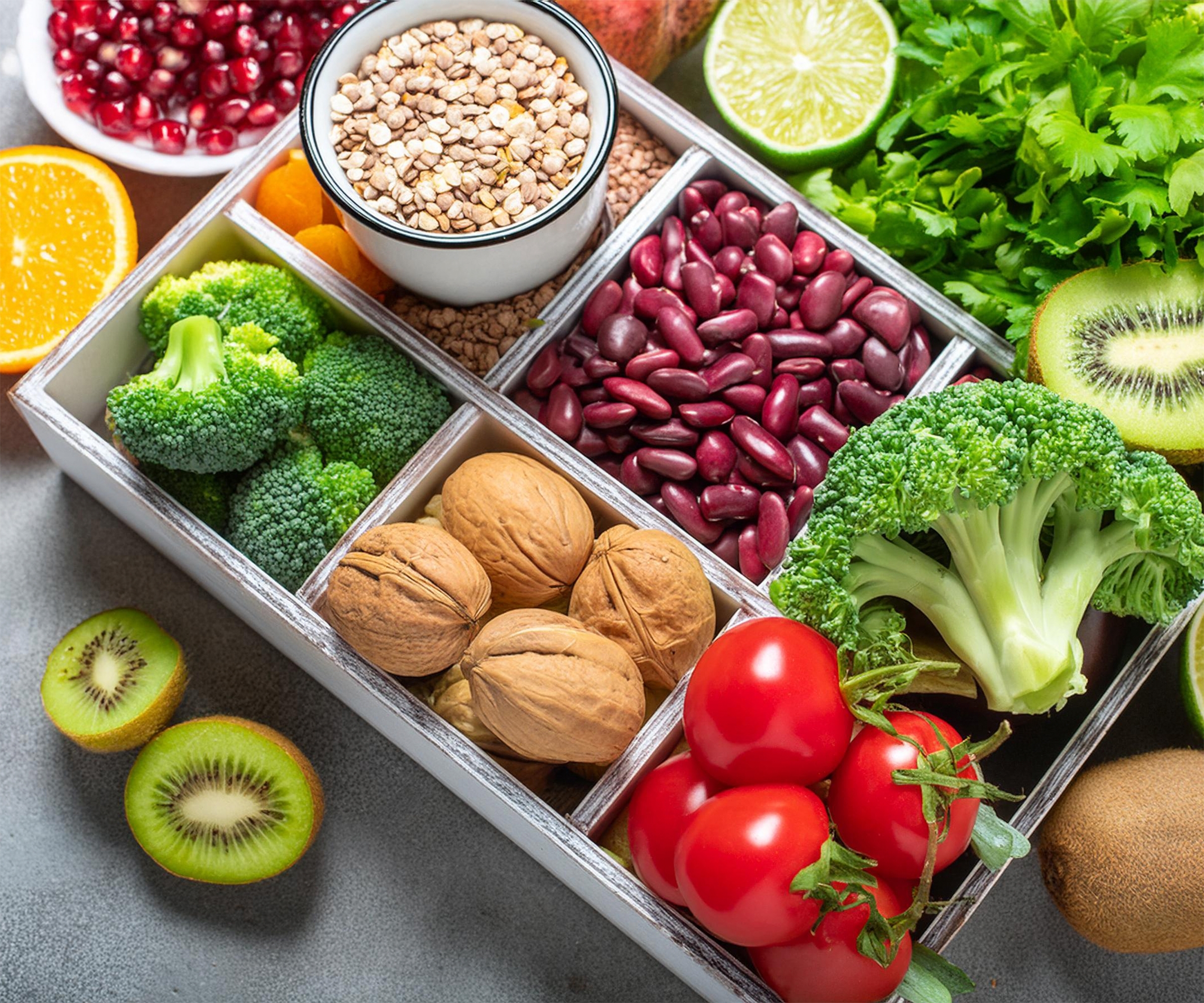
- The DASH diet produces average systolic reductions of 6.97 mm Hg through fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Aerobic exercise at 150 minutes weekly combined with weight loss delivers measurable cardiovascular improvements
- Potassium-rich foods like bananas and spinach lower blood pressure by 5-7 points by regulating sodium and relaxing blood vessel walls
- Meditation and deep breathing exercises provide high-quality evidence for blood pressure reduction through nervous system relaxation
- Combining multiple interventions produces greater reductions than single strategies alone
The DASH Diet: Your Most Powerful Dietary Weapon
The DASH diet stands as the most effective dietary intervention for blood pressure control, supported by high-quality clinical evidence. This eating approach emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while eliminating saturated fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars. Research demonstrates DASH superiority over standard care, delivering average systolic reductions of 6.97 mm Hg. The mechanism works through nutrient density and electrolyte balance, creating sustained cardiovascular improvements without restrictive calorie counting.
Implementation requires no special supplements or expensive programs. Start by filling half your plate with vegetables and fruits, one quarter with whole grains, and one quarter with lean protein sources. This simple visual framework transforms eating habits without overwhelming dietary overhaul. The beauty of DASH lies in its sustainability; you’re not eliminating foods but replacing processed options with whole alternatives that naturally lower blood pressure.
Movement Matters: Aerobic Exercise and Weight Loss Synergy
Moderate to high-quality evidence supports aerobic exercise as a cornerstone blood pressure reduction strategy. The clinical target is 150 minutes of cardiovascular activity weekly—roughly 30 minutes five days per week. Walking, cycling, swimming, and running all qualify. Exercise proves particularly potent when combined with weight loss, though maintaining reduced weight remains the genuine challenge for most people attempting lifestyle modification.
The cardiovascular system responds to consistent aerobic training by improving vessel elasticity and reducing peripheral resistance. Your heart becomes more efficient, requiring less force to pump blood throughout your body. This physiological adaptation translates to measurable blood pressure reductions within weeks of consistent activity, making exercise one of the most reliable non-pharmaceutical interventions available.
Minerals That Relax Your Vessels: Potassium, Magnesium, and Calcium
Potassium regulates sodium levels and relaxes blood vessel walls, enabling improved blood flow and pressure reduction. Studies confirm that increasing potassium-rich foods—bananas, oranges, sweet potatoes, spinach, and beans—lowers blood pressure by 5-7 points. However, individuals with kidney disease or those taking potassium-retaining medications must consult healthcare providers before increasing intake to avoid dangerous electrolyte imbalances.
Magnesium directly relaxes blood vessels and appears abundantly in leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, legumes, salmon, and tofu. Calcium supports blood vessel function through dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based alternatives. Both minerals carry moderate to high-quality evidence supporting their blood pressure-lowering effects, making them essential components of any natural hypertension management strategy.
Fiber and Gut Health: The Overlooked Connection
Dietary fiber feeds healthy gut bacteria, which produce short-chain fatty acids that lower blood pressure through mechanisms still being fully understood by researchers. The recommended daily intake is 25-35 grams, found in whole grains, fruits, vegetables with edible skins, and legumes. Low-calorie diets incorporating increased fiber showed systolic reductions of 4.56-7.78 mm Hg, demonstrating measurable cardiovascular benefits from this simple dietary adjustment.
Watch:
Stress Reduction Through Meditation and Breathing
Meditation and deep breathing exercises promote relaxation, slow heart rate, and lower blood pressure through parasympathetic nervous system activation. High-quality evidence supports meditation as an effective intervention, with moderate-quality evidence backing breathing-control techniques. These practices cost nothing, require no equipment, and deliver results within minutes of consistent practice, making them accessible to virtually anyone regardless of age or fitness level.
Additional Proven Interventions Worth Implementing
Omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts, and chia seeds slow plaque buildup in blood vessels. Nitrates from leafy greens, berries, and beets convert to nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessel walls. Hibiscus tea shows particular benefit for systolic reduction in mild hypertension cases. Isometric training and tai chi demonstrate moderate to high effectiveness, with tai chi producing the largest systolic reduction at 12.75 mm Hg among exercise modalities.
The Multiplier Effect: Combining Strategies
Combining multiple interventions—diet, exercise, weight loss, and stress reduction—produces greater blood pressure reductions than single strategies alone. For overweight and obese individuals, low-calorie diets combined with exercise prove more effective than exercise in isolation. This synergistic approach leverages multiple physiological pathways simultaneously, creating compounding cardiovascular benefits that often exceed pharmaceutical interventions for mild to moderate hypertension cases.
The clinical evidence supporting these interventions comes from high and moderate-quality systematic reviews and network meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. DASH and meditation received the highest quality ratings, establishing them as first-line natural interventions. Your path to lower blood pressure doesn’t require pharmaceutical dependence when science confirms these accessible, sustainable strategies deliver measurable results.
Sources:
Foods That Can Lower Your Blood Pressure Naturally
Natural Ways to Lower Your Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Best High Blood Pressure Supplements
Natural Ways to Lower Your Blood Pressure
How to Lower High Blood Pressure
Lower Blood Pressure Naturally